wind <- read.csv("wind.csv")
head(wind)| i | x | y | |
|---|---|---|---|
| <int> | <dbl> | <dbl> | |
| 1 | 1 | 5.0 | 1.582 |
| 2 | 2 | 6.0 | 1.822 |
| 3 | 3 | 3.4 | 1.057 |
| 4 | 4 | 2.7 | 0.500 |
| 5 | 5 | 10.0 | 2.236 |
| 6 | 6 | 9.7 | 2.386 |
김보람
May 25, 2023
해당 자료는 전북대학교 이영미 교수님 2023응용통계학 자료임
| i | x | y | |
|---|---|---|---|
| <int> | <dbl> | <dbl> | |
| 1 | 1 | 5.0 | 1.582 |
| 2 | 2 | 6.0 | 1.822 |
| 3 | 3 | 3.4 | 1.057 |
| 4 | 4 | 2.7 | 0.500 |
| 5 | 5 | 10.0 | 2.236 |
| 6 | 6 | 9.7 | 2.386 |
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(y~x, wind, pch=16, main="scatter plot")
abline(wind_fit, col='darkorange', lwd=2)
plot(fitted(wind_fit), rstandard(wind_fit), pch = 16,
xlab = expression(hat(y)),
ylab = "Standardized Residuals",
main = "Fitted vs. Residuals")
abline(h = 0, col = "grey", lwd = 2, lty=2)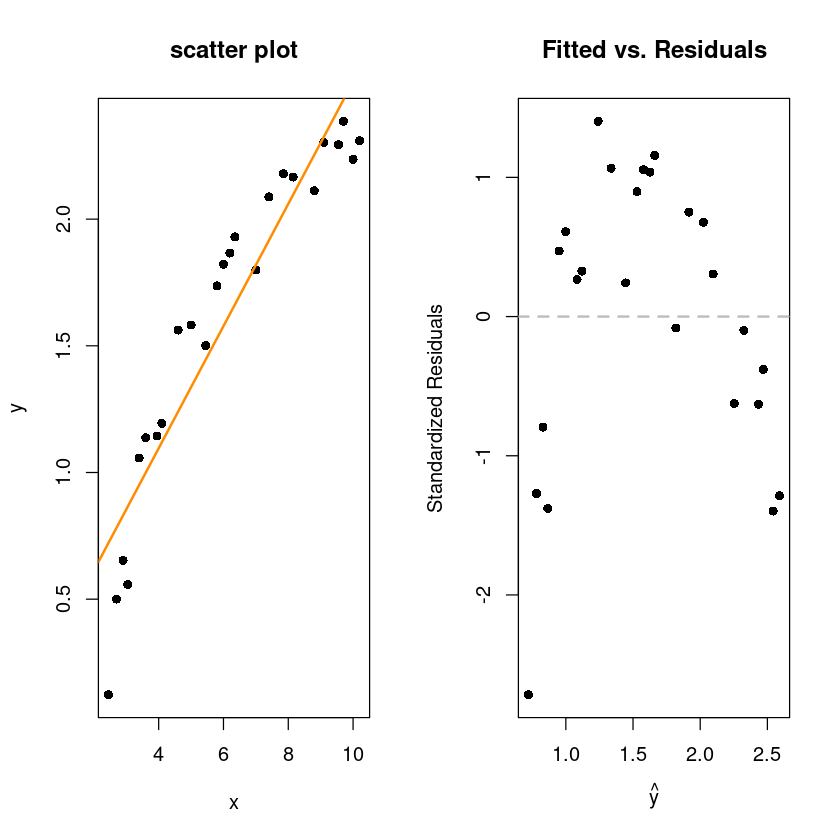
산점도를 봤을때 직선보다는 곡선이 어울려 보이는 산점도
표준화된잔차를 봐도 선형성(2차)이 보인다.
\(y=\beta_0+\beta_1x+\epsilon\)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x, data = wind)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-0.59869 -0.14099 0.06059 0.17262 0.32184
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 0.13088 0.12599 1.039 0.31
x 0.24115 0.01905 12.659 7.55e-12 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.2361 on 23 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.8745, Adjusted R-squared: 0.869
F-statistic: 160.3 on 1 and 23 DF, p-value: 7.546e-12[1] "coefficient of determination : 0.874"\(y=\beta_0+\beta_1x+\beta_2x^2+\epsilon\)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x + I(x^2), data = wind)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-0.26347 -0.02537 0.01264 0.03908 0.19903
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -1.155898 0.174650 -6.618 1.18e-06 ***
x 0.722936 0.061425 11.769 5.77e-11 ***
I(x^2) -0.038121 0.004797 -7.947 6.59e-08 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.1227 on 22 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.9676, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9646
F-statistic: 328.3 on 2 and 22 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16\(x^2\)을 넣었더니 모형도 유의하고 \(R^2\)의 값도 커짐
두개 변수 모두 유의함
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(y~x, wind, pch=16, main="scatter plot")
x_new <- sort(wind$x)
lines(x_new, predict(wind_fit_2, newdata = data.frame(x=x_new)), col='darkorange', lwd=2)
plot(fitted(wind_fit_2), rstandard(wind_fit_2), pch = 16,
xlab = expression(hat(y)),
ylab = "Standardized Residuals",
main = "Fitted vs. Residuals")
abline(h = 0, col = "grey", lwd = 2, lty=2)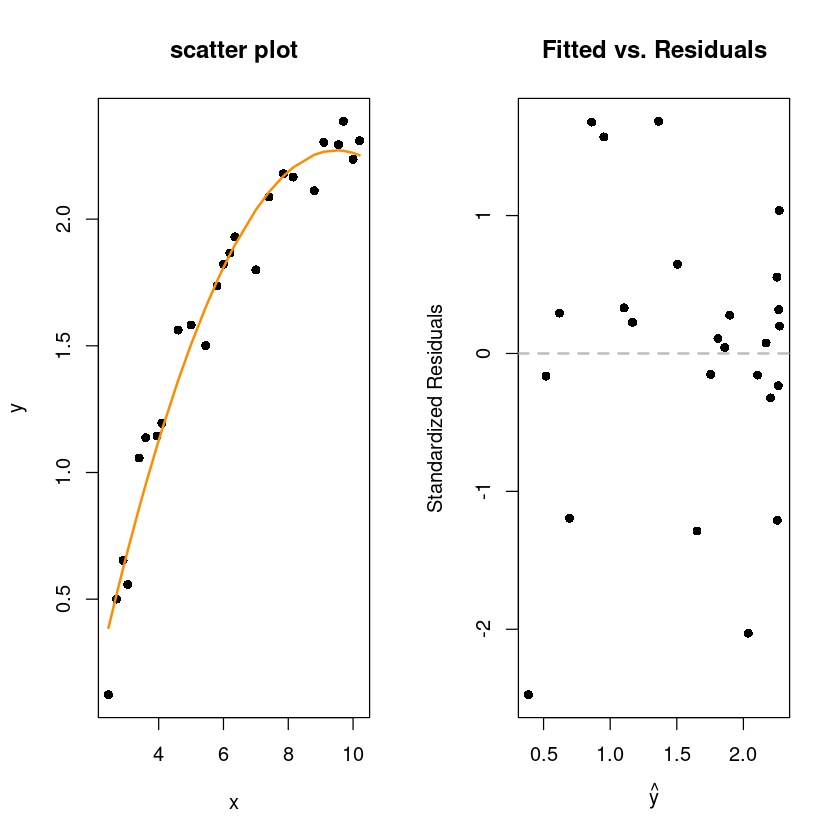
[1] "coefficient of determination : 0.968"\(y=\beta_0+\beta_1 \dfrac{1}{x}+\epsilon=\beta_0+\beta_1 x^`+\epsilon\)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ I(1/x), data = wind)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-0.20547 -0.04940 0.01100 0.08352 0.12204
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 2.9789 0.0449 66.34 <2e-16 ***
I(1/x) -6.9345 0.2064 -33.59 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.09417 on 23 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.98, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9792
F-statistic: 1128 on 1 and 23 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(y~I(1/x), wind, pch=16, main="scatter plot")
abline(wind_fit_3, col='darkorange', lwd=2)
plot(fitted(wind_fit_3), rstandard(wind_fit_3), pch = 16,
xlab = expression(hat(y)),
ylab = "Standardized Residuals",
main = "Fitted vs. Residuals")
abline(h = 0, col = "grey", lwd = 2, lty=2)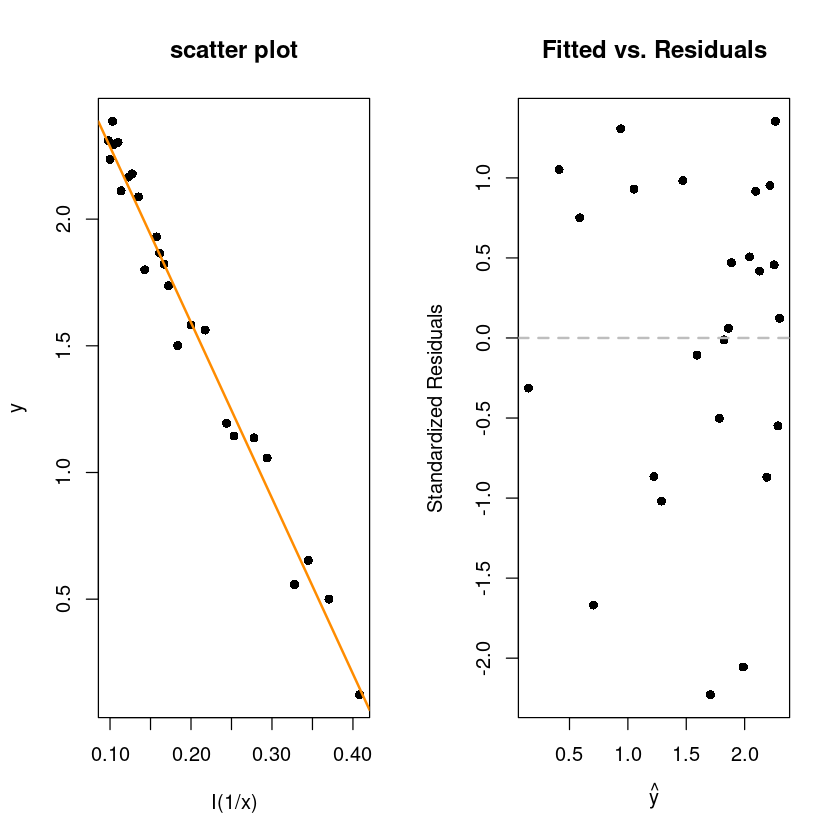
[1] "coefficient of determination : 0.98"| years | salary | |
|---|---|---|
| <int> | <int> | |
| 1 | 1 | 41504 |
| 2 | 1 | 32619 |
| 3 | 1 | 44322 |
| 4 | 2 | 40038 |
| 5 | 2 | 46147 |
| 6 | 2 | 38447 |
곡선 관계!?
x가 증가하면서 y값이 점점 퍼지고 있다. x가 증가할수록 salary의 분산이 커지고 있다.
\(y=\beta_0+\beta_x+\epsilon\)
Call:
lm(formula = salary ~ years, data = initech)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-57225 -18104 241 15589 91332
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 5302 5750 0.922 0.359
years 8637 389 22.200 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 27360 on 98 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.8341, Adjusted R-squared: 0.8324
F-statistic: 492.8 on 1 and 98 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(fitted(initech_fit), rstandard(initech_fit), pch = 16,
xlab = expression(hat(y)),
ylab = "Standardized Residuals",
main = "Fitted versus Residuals")
abline(h = 0, col = "grey", lwd = 2, lty=2)
qqnorm(resid(initech_fit), pch=16,
main = "Normal Q-Q Plot", col = "darkgrey")
qqline(resid(initech_fit), col = "dodgerblue", lwd = 2)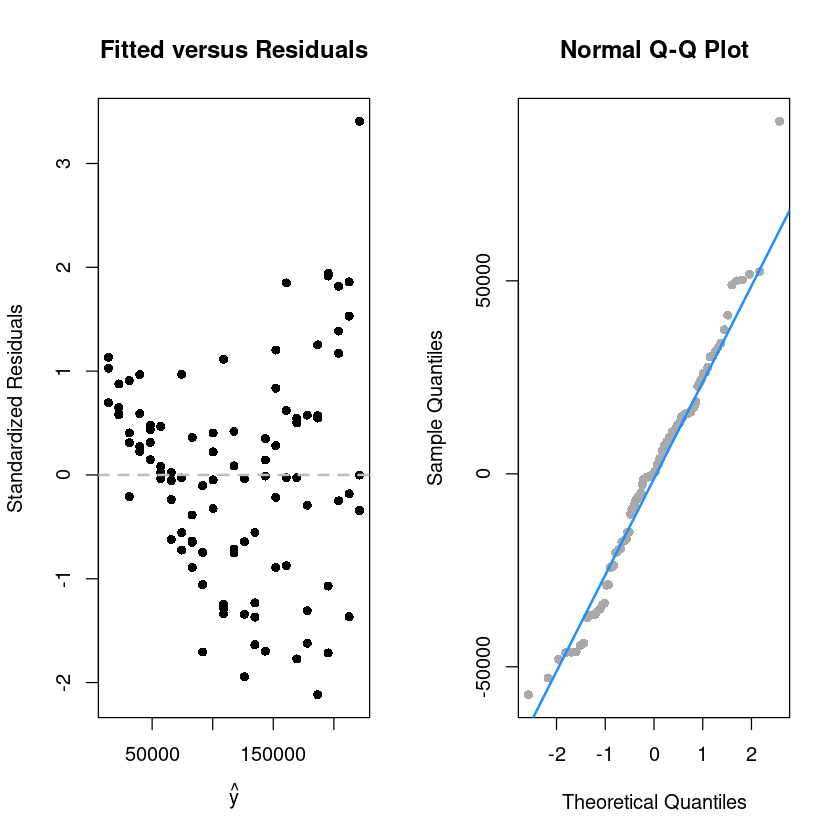
Loading required package: zoo
Attaching package: ‘zoo’
The following objects are masked from ‘package:base’:
as.Date, as.Date.numeric
Durbin-Watson test
data: initech_fit
DW = 1.3313, p-value = 0.0004993
alternative hypothesis: true autocorrelation is not 0등분산성 만족하지 않는다.
변수변환(log y),WLSE -> GLS 를 한다.
Call:
lm(formula = log(salary) ~ years, data = initech)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-0.57022 -0.13560 0.03048 0.14157 0.41366
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 10.48381 0.04108 255.18 <2e-16 ***
years 0.07888 0.00278 28.38 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.1955 on 98 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.8915, Adjusted R-squared: 0.8904
F-statistic: 805.2 on 1 and 98 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16로그변환을 한 모형이므로 RMSE가 작다고 엇 작네 하면 안돼 .y를 예측하는 것과 y`을 예측하는것은 다르다.
\(log \hat y = \hat y^` = \hat \beta_0 + \hat \beta_1 x_1\)
\(\rightarrow \hat y = exp(\hat y^`)\) 역변환 해줘야함
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(log(salary)~years, initech,
pch=16, cex=1.5)
abline(initech_fit_log, col='darkorange', lwd=2)
plot(salary~years, initech,pch=16, cex=1.5)
lines(initech$years,exp(fitted(initech_fit_log)), col="darkorange", lwd=2)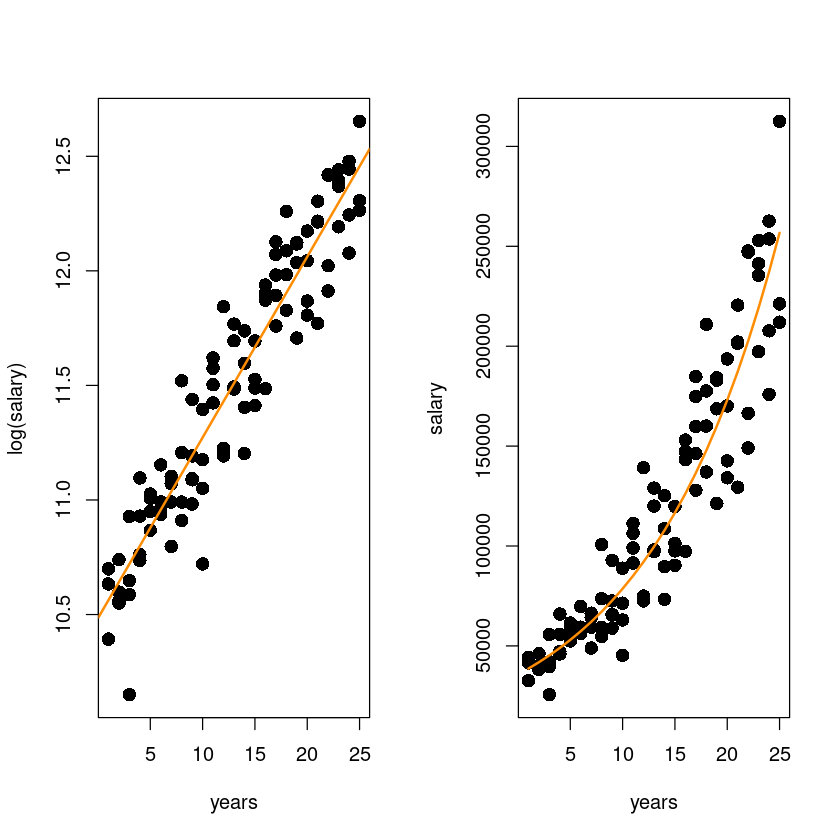
왼쪽 그림: \(\hat y^` = \hat {log y}\)
오른쪽 그림: \(\hat y = exp(\hat \beta_0 + \hat \beta_1x)\)
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plot(fitted(initech_fit_log), rstandard(initech_fit_log), pch = 16,
xlab = expression(hat(y)),
ylab = "Standardized Residuals",
main = "Fitted versus Residuals")
abline(h = 0, col = "grey", lwd = 2, lty=2)
qqnorm(resid(initech_fit_log), pch=16,
main = "Normal Q-Q Plot", col = "darkgrey")
qqline(resid(initech_fit_log), col = "dodgerblue", lwd = 2)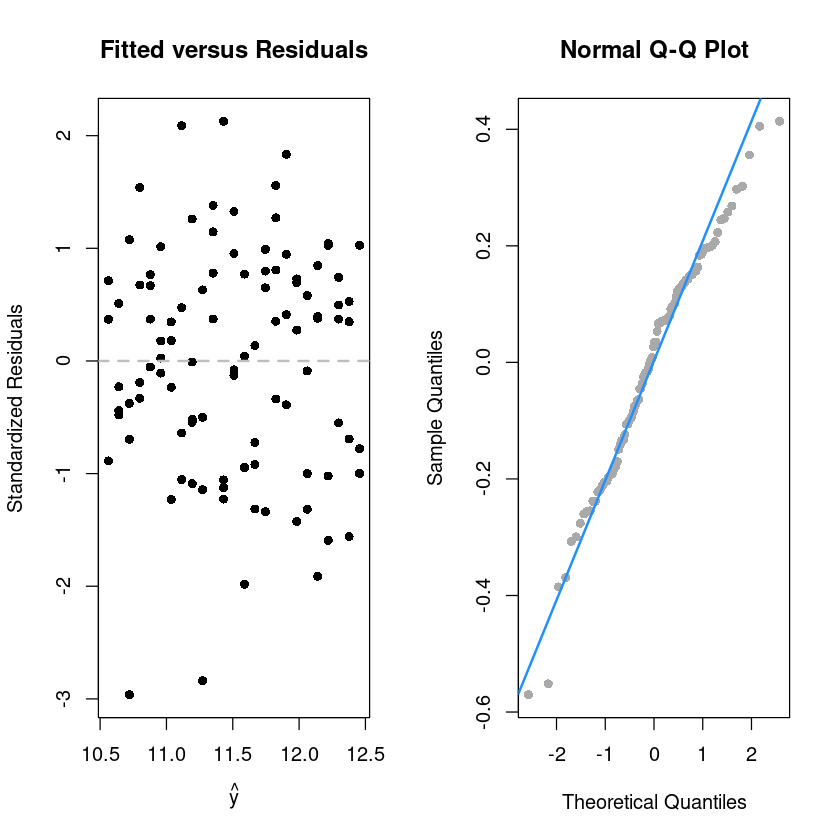
\(y=\beta_0+\beta_x+\epsilon\)
\(log y = \beta_0+\beta_1x+\epsilon\)
\(\sqrt{MSE}=\hat \sigma\) -LM1
\(\sqrt{MSE}=\hat \sigma\) -LM2
\(y-(exp(\hat{log y})=\hat y)\)
\(y'=log y\)
log변환은 앞쪽은 작게 압축시키고 뒤쪽은 확 압축시킴
log변환과 다르게 덜 압축하는 방법??? sqrt로 압축..
지수변환 \(\lambda\)파라미터를 이용해서 변환.. (일반화..)
\[y'=g_{\lambda}(y)= \begin{cases} \dfrac{y^{\lambda}-1}{\lambda} & \lambda \neq 0 \\ log y & \lambda=0 \end{cases}\]
(-2,2)가 기본으로 보여줌
0을 좌우로 점선은 \(\lambda\)의 95% 신뢰구간
log-Likeilihood를 이용하여 가장 큰 \(\lambda\)를 찾아준다.
\(\lambda\)를 결정해주는 함수->boxcox
가장 큰 \(\hat \lambda\) 은 0.08… 근데 의미가 없음.. 신뢰구간에 0이 들어가있네? 0은 로그변환이니까 0도 괜찮겠다!